
This may be the case if the company has sustained long-term losses or if its dividends exceed its profits. On the other hand, when a company generates surplus income, a portion of the long-term shareholders may expect some regular income in the form of dividends as a reward for putting their money into the company. Traders who look for short-term gains may also prefer dividend payments that offer instant gains. In the long run, such initiatives may lead to better returns for the company shareholders instead of those gained from dividend payouts. Paying off high-interest debt also may be preferred by both management and shareholders, instead of dividend payments. Management and shareholders may want the company to retain earnings for several different reasons.

Retained Earnings: Everything You Need to Know for Your Small Business
As a result, each shareholder has additional shares after the stock dividends are declared, but their stake remains the same. Retained earnings appear on the liability side of your company’s balance sheet under shareholders’ equity and act as an important source of self-financing or internal financing. It can reinvest this money into the business for expansion, operating expenses, research and development, acquisitions, launching new products, and more.
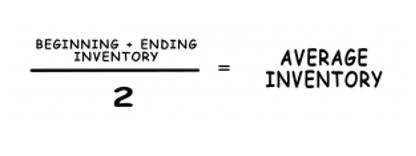
Find the beginning equity on your balance sheet

Let’s face it—managing finances isn’t always the most exciting part of running your business. But bookkeeping as an entrepreneur, startup founder, or small business owner, clarity around your company’s financial health is essential. A critical part of this clarity comes from understanding your company’s statement of retained earnings.
- But as an entrepreneur, startup founder, or small business owner, clarity around your company’s financial health is essential.
- Retained earnings appear on the liability side of your company’s balance sheet under shareholders’ equity and act as an important source of self-financing or internal financing.
- Retained earnings appear under the shareholder’s equity section on the liability side of the balance sheet, and often companies will show this as a separate line item.
- This statement begins with the opening balance of retained earnings, adds the net income for the period, and subtracts any dividends paid out.
- Retained earnings represent the portion of your company’s net income that remains after dividends have been paid to your shareholders, and is reinvested or ‘ploughed back’ into the company.
- The following are four common examples of how businesses might use their retained earnings.
What is the Retained Earnings Formula?
- For financial professionals, a comprehensive understanding of retained earnings is indispensable for executing effective financial planning and analysis (FP&A) strategies.
- If they are confident that this surplus income can be reinvested in the business, then it can create more value for the stockholders by generating higher returns.
- These statements report changes to your retained earnings over the course of an accounting period.
- While essential for building financial strength and flexibility, retained earnings differ fundamentally from tangible assets such as cash, inventory, or property.
- Examples of these items include sales revenue, cost of goods sold, depreciation, and other operating expenses.
- Also, keep in mind that the equation you use to get shareholders’ equity is the same you use to get your working capital.
Accounting standards like GAAP and IFRS require transparent disclosure of adjustments to retained earnings, whether due to prior period errors or policy changes. This transparency fosters trust and ensures stakeholders understand equity changes. Tax considerations, such as deferred tax liabilities, must also be managed to optimize shareholder value. When a company changes its reporting entity due to mergers, acquisitions, or divestitures, financial statements must be restated to reflect the new configuration. Transparency in these adjustments is vital, as they significantly impact metrics and ratios used by investors and analysts. Discover the essentials of a retained earnings statement, its components, and its role in reflecting a company’s financial health.
What Are Private Goods? Definition, Examples, and Key Accounting Factors

If they are confident that this surplus Insurance Accounting income can be reinvested in the business, then it can create more value for the stockholders by generating higher returns. It’s important to note that retained earnings are cumulative, meaning the ending retained earnings balance for one accounting period becomes the beginning retained earnings balance for the next period. A statement of retained earnings details the changes in a company’s retained earnings balance over a specific period, usually a year. Generally speaking, a company with a negative retained earnings balance would signal weakness because it indicates that the company has experienced losses in one or more previous years. When the retained earnings balance is less than zero, it is referred to as an accumulated deficit.

- Dividends, the portion of earnings returned to shareholders, directly reduce retained earnings.
- Effective leadership can drive operational efficiencies, cost management, and strategic investments, all of which contribute to healthier retained earnings.
- Retained earnings represent the cumulative net income of a company that has been prudently reserved for reinvestment rather than distributed to shareholders in the form of dividends.
- Retained earnings represent the cumulative profits the company has kept after distributing dividends to shareholders.
- When they know that management has profitable investment opportunities and have faith in the management’s capabilities, they will want management to retain surplus profits for higher returns.
Retained earnings are a type of equity and are therefore reported in the shareholders’ equity section of the balance sheet. Although retained earnings are not themselves an asset, they can be used to purchase assets such as inventory, equipment, or other investments. Therefore, a company with a large retained earnings balance may be well-positioned to purchase new assets in the future or offer increased dividend payments to its shareholders. The beginning retained earnings in a financial statement represent the accumulated retained earnings balance at the start of the accounting period. Understanding the composition and changes in retained earnings is vital for stakeholders to assess the company’s financial performance and future prospects. Companies may choose to distribute dividends in the form of cash or stock dividends, using the surplus from their retained retained earnings represents earnings.

Leave a Reply